compiled by Arlene & David Kaplan
Did Astronomers See a Star Explode Twice? Astronomers may have spotted their first superkilonova — a star that’s exploded not once, but twice. When massive stars die, they detonate in a celestial fireworks display known as a supernova. Often this leaves behind a neutron star — a dense, city-sized kernel. A spoonful of its material weighs more than everyone on Earth put together…more
Explore Orion’s Massive New Stars with Binoculars Some constellations have all the luck. Orion not only has one of the most recognizable forms, including its signature Belt, but it contains two of the top 10 brightest nighttime stars (Rigel and Betelgeuse), three 2nd-magnitude stars and M42, the Orion Nebula, one of the brightest and most important star-forming regions in the galaxy. No wonder it sparkles on winter nights…more
The Sticky Problem of Lunar Dust Gets a Mathematical Solution Apollo astronauts discovered an unexpected enemy on the Moon. Fine dust, kicked up by their movements and attracted by static electricity, coated everything. It found its way through seals, scratched visors, and clung to suits despite vigorous brushing. Eugene Cernan described it as one of the most aggravating aspects of lunar operations…more
When Stars Fail to Explode Many stars die spectacularly when they explode as supernovae. During these violent explosions, they leave behind thick, chaotic clouds of debris shaped like cauliflowers. But supernova remnant Pa 30 looks nothing like that. Instead of the usual remains, long, straight filaments radiate from a central point of Pa 30 like trails from a sparkler frozen mid-burst…more
Space Mice Come Home and Start Families Four mice went to space as astronauts. One came back and became a mother. And that simple fact might matter more than you’d think for humanity’s future beyond Earth. On 31 October, China launched four mice numbered 6, 98, 154, and 186, aboard the Shenzhou-21 spacecraft to the country’s space station, roughly 400 kilometers above Earth…more
A Pioneering Study Assesses the Likelihood of Asteroid Mining A few years ago, asteroid mining was all the rage. With the commercial space sector rapidly growing, the dream of commercializing space seemed almost imminent. Basically, the notion of having platforms and spacecraft that could rendezvous and mine Near Earth Asteroids (NEAs), then return them to space-based foundries, was right up there with sending commercial crews to Mars…more
Finding runaway stars to help map dark matter in the Milky Way Hypervelocity stars have, since the 1920s, been an important tool that allows astronomers to study the properties of the Milky Way galaxy, such as its gravitational potential and the distribution of matter. Now astronomers from China have made a large-volume search for hypervelocity stars by utilizing a special class of stars…more
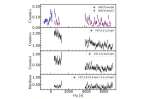
Einstein Probe detects an X-ray flare from nearby star Using the Einstein Probe (EP), astronomers have detected a new X-ray transient event, which turned out to be an X-ray flare from the star PM J23221-0301 located about 150 light years away. The finding was reported in a research paper published December 18 on the arXiv preprint server…more
NASA’s Chandra rings in the new year with the Champagne Cluster Celebrate the New Year with the “Champagne Cluster,” a galaxy cluster seen in this new image from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and optical telescopes. Astronomers discovered this galaxy cluster on Dec. 31, 2020. The date, combined with the bubble-like appearance of the galaxies and the superheated gas seen with Chandra observations…more
Astronomers may finally have worked out what the Star of Bethlehem was, and why it behaved so strangely in the sky A group of astronomers believe they may have finally worked out what the ‘Star of Bethlehem’ really was, and how to account for its strange behavior, as described in the the Gospel of Matthew. The mystery of the ‘Christmas Star’, or the ‘Star of Bethlehem‘, is one that continues to intrigue historians of astronomy…more
Scientists found a surprise in plumes erupting from this icy moon. It could be a major leap in the search for life Enceladus is a medium-sized moon of Saturn made up of a crust of water-ice and an ocean of liquid water below. The moon’s ocean is similar to those on Earth and is connected directly to Enceladus’s rocky core…more
NASA’s Webb Observes Exoplanet Whose Composition Defies Explanation Scientists using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have observed a rare type of exoplanet, or planet outside our solar system, whose atmospheric composition challenges our understanding of how it formed. Officially named PSR J2322-2650b, this Jupiter-mass object appears to have an exotic helium-and-carbon-dominated atmosphere unlike any ever seen before…more